-
Author
Monica Le -
PI
Irena Tsui, MD
-
Co-Author
Monica Le, Sahar Ashrafzadeh, Robert Gunzenhauser
-
Title
Teleretinal Screening with Optical Coherence Tomography During the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
Program
STTP
-
Other Program (if not listed above)
-
Abstract
Background
In 2019, a novel teleretinal imaging program was implemented at the Veteran Affairs (VA) Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System providing access to teleophthalmologic consult, integrating remote OCT evaluation and retinal specialist. The population of patients who utilized the teleretinal services reflected the most vulnerable including those with cardiometabolic conditions, psychiatric conditions, and individuals experiencing homelessness[1]. Previous evaluation of the 158 tele-OCT consults showed compliance with recommended follow up was 76.4% and over half of teleretinal consults requested both diagnosis and management[1]. This project continues to evaluate the utilization of the pilot teleOCT program during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and its impact on eye care at the Veteran Health Administration (VHA).
Objective
To evaluate and assess the utilization of a pilot teleretinal imaging program and its clinical impact at the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System during COVID-19 2020 pandemic.
Methods
Retrospective chart review study using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS). Inclusion criteria: all patients evaluated using the teleretinal imaging program with OCT imaging. REDCap was used for data collection and management [2]. Variables collected: patient demographic data, medical history, teleretinal consult results and referrals, and patient adherence. We will analyze potential association between age, housing status, co-morbidities, ocular health, psychiatric conditions, driving distance to eye clinic with compliance rate within 2020 and between 2019 and 2020 results. SPSS statistical software will be used for data analysis, and statistical significance will be determined at p < 0.05(*) [3].
Results
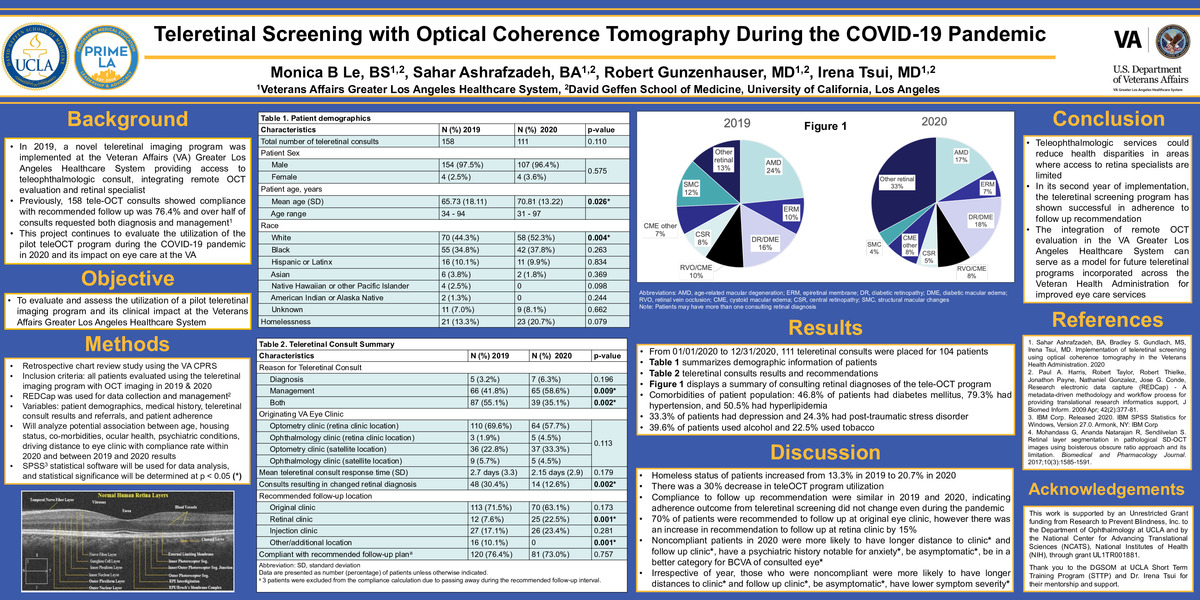
From 01/01/2020 to 12/31/2020, a total of 111 teleretinal consults were placed for 104 patients. Table 1 summarizes demographic information of patients who utilized the teleretinal screening program in 2019 and 2020. Table 2 presents 2019 and 2020 teleretinal consults results and recommendations. Comorbidities of patient population: 46.8% of patients had diabetes mellitus, 79.3% had hypertension, and 50.5% had hyperlipidemia. 33.3% of patients had depression and 24.3% had post-traumatic stress disorder. 39.6% of patients used alcohol and 22.5% used tobacco. Figure 1 displays a summary of consulting retinal diagnoses of the tele-OCT program.
Discussion
Veteran patients were predominately male and elderly; homeless status of patients increased from 13.3% in 2019 to 20.7% in 2020. In 2020, there was a 30% decrease in teleOCT program utilization; possibly due to decrease in optometry visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Patients in 2020 were more likely to be older and have White as their selected race. Compliance to follow up recommendation were similar in 2019 and 2020, indicating adherence outcomes from teleretinal screening did not change even during the pandemic. 70% of patients were recommended to follow up at the original eye clinic, however, there was an increase in recommendation to follow up at retina clinic by 15% in 2020. Noncompliant patients in 2020 were more likely to have a longer distance to clinic* and follow up clinic*, have a psychiatric history notable for anxiety*, be asymptomatic*, be in a better category for BCVA of consulted eye*. Irrespective of the year, those who were noncompliant were more likely to have longer distances to clinic* and follow up clinic*, be asymptomatic*, have lower symptom severity*.
Conclusion
Teleophthalmologic services could reduce health disparities in areas where access to retina specialists is limited and when traveling to consultations are barriers in receiving eye care. In its second year of implementation, the teleretinal screening program has shown success in adherence to follow up recommendations among the veteran population and in saving time and travel to retina clinic for consult. The integration of remote OCT evaluation in the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System can serve as a model for future teleretinal programs incorporated across the Veteran Health Administration for improved eye care services.
-
PDF
-
Zoom
https://uclahs.zoom.us/j/93742166568?pwd=bUlrYmlGQ1NKdi84QWNFNVN2TmVaQT09