-
Author
Anjali Pradhan -
PI
Claire Karekezi, MD and Isaac Yang, MD
-
Co-Author
François Xavier Rutayisire MD, Paulin Munyemana MD
-
Title
Unusual Intracranial Suppuration: 2 Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
-
Program
Global Short-Term Training Program
-
Other Program (if not listed above)
-
Abstract
Background:
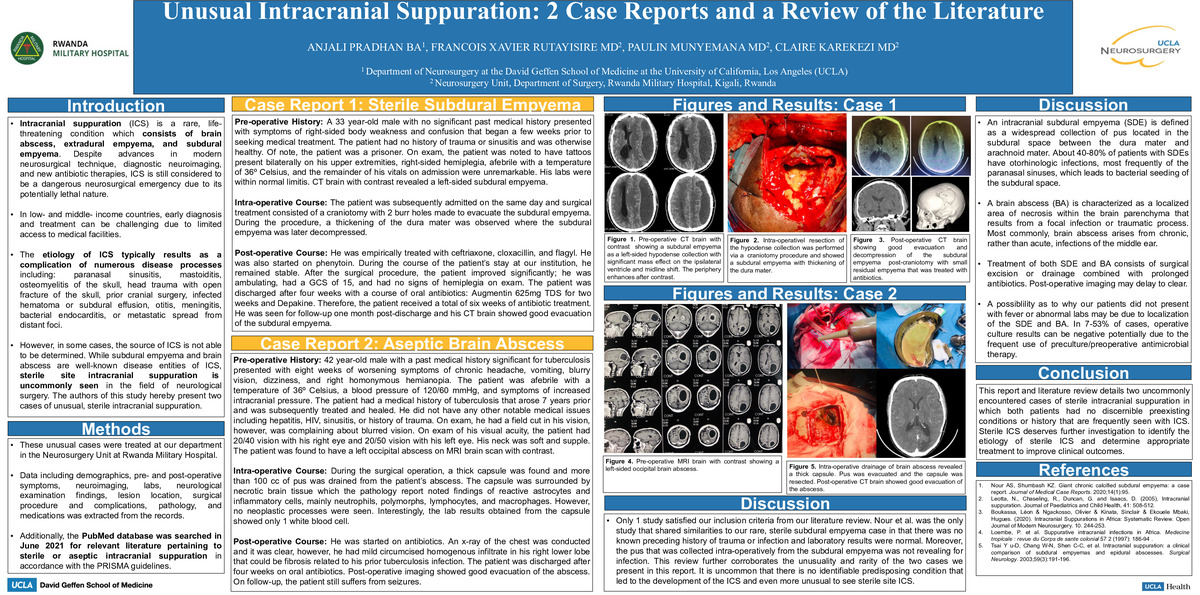
Intracranial suppuration (ICS) is a rare complication that can arise from various disease processes and is comprised of brain abscess, extradural empyema, and subdural empyema. Although significant progress has been achieved regarding the development of antibiotics, neuroimaging, and neurosurgical technique, ICS remains to be a serious neurosurgical emergency that requires timely diagnosis and management. An uncommon presentation of ICS is sterile intracranial suppuration which has yet to be fully elucidated by clinicians. The authors hereby present two cases of unusual sterile intracranial suppuration: a sterile subdural empyema and a sterile brain abscess.
Methods:
The authors present two patient cases of unusual, sterile intracranial suppuration. Data including demographics, pre- and post-operative symptoms, neuroimaging, labs, neurological examination findings, lesion location, surgical procedure and complications, pathology, and medications was extracted from the records. The PubMed database was searched in June 2021 for relevant literature pertaining to sterile or aseptic intracranial suppuration in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines.
Results:
Both patients underwent surgical treatment consisting of craniotomy to evacuate the pus collection. The blood cultures from both the patients, the collected empyema, and the thick capsule from the brain abscess were sterile. However, the necrotic brain tissue surrounding the abscess contained inflammatory cells. Both patients were treated empirically with antibiotics. During the course of their stay, both patients remained stable and no complications were observed, except for the patient with brain abscess who developed seizures post-operatively.
Conclusion:
Sterile ICS is a disease entity that warrants further investigation to determine appropriate treatment to improve patient outcomes. This study highlights the paucity of data available regarding sterile ICS and supports the need for future studies to uncover the etiology of sterile ICS so as to better guide management of this condition.
-
PDF
-
Zoom
https://uclahs.zoom.us/j/93080217250?pwd=dk9NQVJ3ZU9LVVhmQjhmWTB0NWFJZz09