-
Author
Ramita Karra -
Poster Title
Effects of A Multi-Pronged Wellness Intervention on Neurology Resident Burnout
-
Author(s)
Ramita D. Karra, MD, Katherine Fu, MD, Adrienne Keener, MD
-
Contact Author Email
rkarra@mednet.ucla.edu
-
Poster Abstract
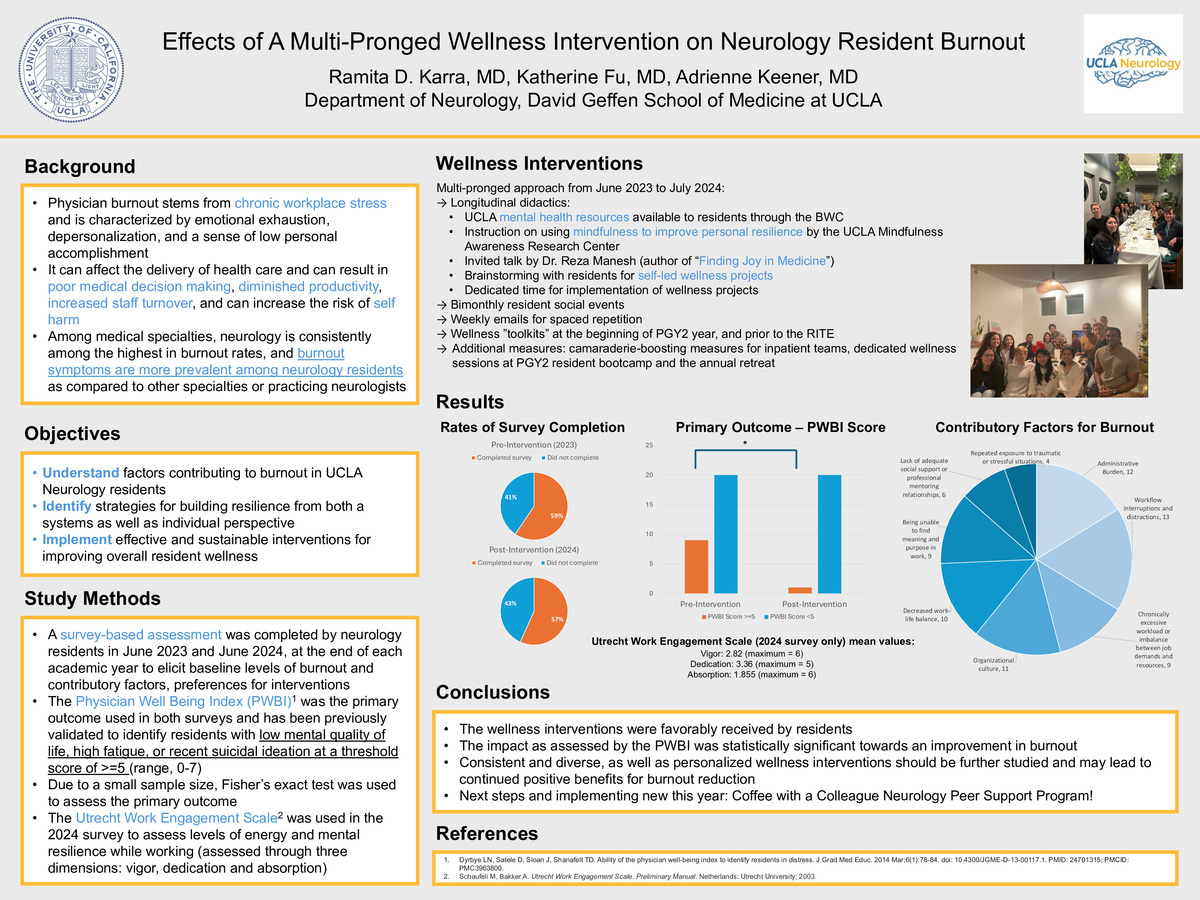
Burnout stems from chronic workplace stress and is characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a sense of low personal accomplishment. The objective of this study was to understand factors contributing to burnout in neurology residents, and the effectiveness of systems based as well as individual approaches. This nonrandomized preintervention and postintervention study was conducted at a single academic-based neurology residency program from June 2023 to June 2024, and included residents in postgraduate years 2, 3, and 4. The intervention was a multi-pronged wellness program including longitudinal didactics, bimonthly resident social events, weekly emails for spaced repetition, and general measures such as a dedicated wellness session at the annual retreat. Longitudinal didactics consisted of 5 1-hour blocks for topics including institutional mental health resources, mindfulness meditation, finding meaning in medicine, and resident self-led projects. The Physician Well Being Index (PWBI) was the primary outcome used in both surveys and has been previously validated to identify residents with low mental quality of life, high fatigue, or recent suicidal ideation at a threshold score of >=5 (range, 0-7). Due to a small sample size, Fisher’s exact test was used to assess the primary outcome. Of 37 eligible residents, 22 completed the preintervention survey (59% response rate), and 21 completed the postintervention survey (57% response rate). In the preintervention survey, 9/22 residents (41%) had a PWBI score >=5 (mean 3.5), as compared to 1/21 residents (5%] (mean 2.4) in the postintervention survey (p=0.01). Overall, the wellness interventions were favorably received by residents and the impact as assessed by the PWBI was statistically significant towards an improvement in burnout. These results suggest that consistent and diverse wellness interventions should be further studied and may lead to a positive impact in burnout reduction.
-
Keywords
Medical education, Curriculum, Wellness
-
Poster PDF